Multimodal ai - How it all works!
Multimodalities
Multimodal GEN AI - Text, Audio, Image/Video
LLMs
Get in the weeds a bit with LLMs
LLMs
Get in the weeds a bit with LLMs
Generate excitement
What's something exciting your business offers? Say it here.
Generate excitement
What's something exciting your business offers? Say it here.
AI Capability Models
Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) Model
AI Models Explained
GANS
To understand GANs, you must first understand the terms generative and adversarial.
- A generative adversarial network (GAN) is a class of machine learning frameworks and a prominent framework for approaching generative artificial intelligence. The concept was initially developed by Ian Goodfellow and his colleagues in June 2014.[1] In a GAN, two neural networks contest with each other in the form of a zero-sum game, where one agent's gain is another agent's loss.
- Generative: You can think of the term generative as producing something. This can be taking some input images and producing an output with a twist. For example, you can transform a horse into a zebra with some degree of accuracy. The result depends on the input and how well-trained the layers are in the generative model for this use case.
- Adversarial: You can think of the term adversarial as pitting one thing against another thing. In the context of GANs, this means pitting the generative result (fake images) against the real images present in the data set. The specific mechanism is called a discriminator, which is implementing a model that tries to discriminate between the real and fake images
AGI
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) refers to a type of artificial intelligence that possesses the ability to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a wide range of tasks at a level comparable to human intelligence. Unlike narrow or specialized AI, which is designed to perform specific tasks (like image recognition, playing chess, or language translation), AGI would demonstrate:
- Flexibility: The ability to apply intelligence to any problem, not just those it was specifically designed to solve.
- Cognitive Abilities: Skills such as reasoning, problem-solving, planning, learning from experience, understanding complex concepts, and even creativity and emotional intelligence, akin to human cognitive capabilities.
- Adaptability: The capacity to learn from new contexts without significant preprogramming, adapting to novel situations as a human would.
- Generalization: Understanding and learning from one task to improve performance in another, seemingly unrelated task.
Key Characteristics of AGI:
- Autonomy: AGI systems would operate with a significant degree of independence, making decisions based on their understanding of the world rather than following pre-set algorithms.
- Transfer Learning: The ability to leverage knowledge from one domain to another, which is a hallmark of human learning but still a challenging area for current AI systems.
- Common Sense: Understanding the world in a way that includes common sense reasoning, something that current AI systems struggle with.
Current Status and Challenges:
- Research Frontier: AGI remains a theoretical goal in AI research. While we have made significant strides in narrow AI, true AGI is not yet realized.
- Ethical and Safety Concerns: The development of AGI raises profound questions about control, safety, ethics, and the impact on society, employment, and human identity.
- Technical Hurdles: Achieving AGI involves overcoming numerous challenges in areas like cognitive architectures, machine learning, neural networks, and understanding consciousness and human-like intelligence.
Philosophical and Societal Implications:
- Human-AI Interaction: AGI would potentially lead to new forms of interaction, collaboration, or even competition between humans and machines.
- Regulation and Control: There are ongoing discussions about how AGI should be regulated to ensure it benefits humanity without posing existential risks.
In summary, AGI represents the aspiration to create machines that can think, learn, and act with the breadth and depth of human intelligence, a goal that, while not yet achieved, continues to drive significant research and debate in the field of artificial intelligence.
AI Capabilities, Functionality, Purpose
Here are the main types of Artificial Intelligence categorized by their capabilities, functionality, and purpose:
By Capability:
- Narrow or Weak AI (ANI - Artificial Narrow Intelligence):
- Focuses on a singular or narrow task. Examples include voice assistants like Siri, recommendation systems like those used by Netflix, or image recognition software. They excel at their specific tasks but don't possess general cognitive abilities.
- General AI (AGI - Artificial General Intelligence):
- Hypothetical AI that would have the ability to understand or learn any intellectual task that a human being can. AGI would be capable of flexible and autonomous behavior across different contexts with cognitive abilities akin to humans. This level of AI does not currently exist.
- Superintelligent AI or Strong AI:
- An AI that surpasses human intelligence in all aspects, including creativity, social skills, and general wisdom. This is speculative and a topic of much debate regarding its potential implications for humanity.
By Functionality:
- Reactive Machines:
- AI that can only react to current stimuli, with no memory of past events to inform current decisions. An example is IBM's Deep Blue, which could respond to chess moves but had no memory or learning capability beyond the game.
- Limited Memory AI:
- Can use past experiences to inform present decisions but only for a very limited time. Most modern AI systems, including self-driving cars, fall here as they can observe how other cars move, learn from it, but only for a short duration.
- Theory of Mind AI:
- A more advanced AI that would understand human emotions, beliefs, and thoughts. This level of AI would require profound advances in psychology, cognitive science, and AI, and we are not yet at this stage.
- Self-aware AI:
- The highest level of AI, which would have consciousness, self-awareness, and understand its own existence. This is purely theoretical at this point.
By Purpose:
- Analytical AI:
- Focused on understanding complex data patterns to provide insights, predictions, or decisions. Used in areas like finance, healthcare for diagnostics, or in fraud detection.
- Interactive AI:
- Designed to interact with humans in a natural way, often through language or visual cues. Chatbots, virtual assistants, and some customer service applications fall into this category.
- Text AI:
- Specializes in processing and generating text. This includes natural language processing for translation, sentiment analysis, or content generation.
- Visual AI:
- Deals with image and video processing, recognition, and generation. Applications include facial recognition, autonomous driving systems, and medical image analysis.
- Auditory AI:
- Focuses on sound, from speech recognition to music composition or sound classification in environments.
- Robotic AI:
- Combines AI with robotics, where AI systems control physical robots for tasks ranging from manufacturing to service industries.
These categories are not strictly mutually exclusive, and advancements often blur these lines, with many AI systems incorporating aspects from multiple types.
As AI technology evolves, these classifications might expand or shift to accommodate new developments and applications. Artificial General Intelligence, Machine Learning
.
AI LLM Model Development Progression





GEN AI integration & security in 2025
Grab interest
Say something interesting about your business here.
Generate excitement
What's something exciting your business offers? Say it here.
Integrating AI into an enterprise
AI Enterprise Integration
Integrating AI into an enterprise involves a strategic approach to ensure that the technology aligns with business objectives, enhances efficiency, and drives growth. Here's a step-by-step guide to integrate AI effectively:
1. Assessment and Strategy Development
- Identify Needs: Start by pinpointing areas where AI can add value, like customer service, data analysis, process automation, or decision-making. Look at bottlenecks, repetitive tasks, or areas where AI could provide insights not currently available.
- Define Goals: Set clear, measurable objectives for what you want AI to achieve. This could be cost reduction, improved customer experience, or enhanced decision-making capabilities.
2. Data Preparation
- Data Collection: Ensure you have high-quality, relevant data because AI models learn from data. Address data quality issues, as poor data can lead to poor AI performance.
- Data Integration: Work on connecting different data sources to provide a comprehensive dataset for AI systems. This might involve breaking down data silos.
3. Choosing the Right AI Technology
- Technology Selection: Decide whether to build AI solutions in-house, use off-the-shelf AI products, or opt for a hybrid approach. Consider the scalability, cost, and adaptability of the solution.
- Vendor Assessment: Evaluate AI vendors or platforms based on their capabilities, integration ease, and support for your specific use cases.
4. Pilot Projects
- Start Small: Begin with pilot projects or proofs of concept (POCs) that are low-risk and high-reward. This allows you to test AI's impact in a controlled environment.
- Iterate and Learn: Use feedback from pilot projects to refine AI models or choose different approaches if necessary.
5. Integration and Deployment
- System Integration: Ensure AI can work seamlessly with existing IT systems. This might involve API integration, middleware, or custom development to connect AI with legacy systems.
- Deployment Strategy: Plan for how AI will be rolled out across the enterprise, whether it's gradually or all at once, and consider cloud vs. on-premise deployment.
6. Employee Training and Change Management
- Workforce Enablement: Train employees to work alongside AI systems, understanding both how to use them and how they change existing workflows.
- Cultural Adaptation: Address employee concerns about job displacement by highlighting how AI can enhance their work rather than replace it.
7. Monitoring and Optimization
- Performance Tracking: Implement metrics to evaluate AI's performance against the set objectives. Adjust as necessary based on data-driven insights.
- Continuous Improvement: AI models often require retraining or updating as they encounter new data or as business needs evolve.
8. Ethical and Compliance Considerations
- Ethical AI Use: Ensure AI models are free from bias, respect privacy, and operate within ethical bounds.
- Regulatory Compliance: Stay informed about AI regulations that might affect your industry, like GDPR in Europe or new AI-specific laws emerging globally.
9. Scaling Up
- Strategic Expansion: Once successful in one area, consider how AI can be scaled to other parts of the business. This might mean expanding to new departments or integrating AI more deeply into existing processes.
10. Innovation and Future Planning
- Stay Informed: AI technology evolves rapidly. Keep your strategy flexible to incorporate new AI advancements or shifts in market demands.
- Innovation Culture: Foster a culture where employees are encouraged to experiment with AI in new ways, promoting continuous innovation.
By following these steps, enterprises can navigate the complexities of AI integration, ensuring that AI becomes a beneficial tool that drives business success rather than just an additional layer of technology.
AI ethics in business AI for small businesses more case studies Add an extra layer of security to your login process with our two-factor authentication solutions.
Our solutions require a second factor of authentication, such as a text message or biometric scan, to ensure that only authorized users can access your systems.
See AI Security Defense's Security Solutions in Action: Our Photo Gallery
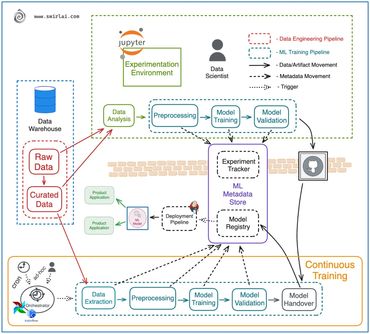
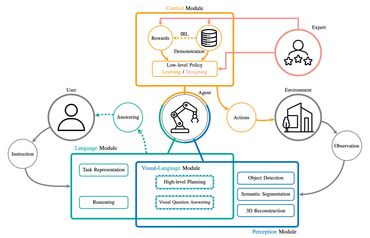
Must have skills to survive in the AI future
AGI coming very soon
AGI is going to explode in 2025!.
Be an AI Generalist
This guy Liam provides some good AI entrepreneurial guidance!
AI Benefits and challenges?
.
Generate excitement
What's something exciting your business offers? Say it here.
Close the deal
Give customers a reason to do business with you.
Grab interest
Say something interesting about your business here.
Generate excitement
What's something exciting your business offers? Say it here.
Close the deal
Give customers a reason to do business with you.
Grab interest
Say something interesting about your business here.
This website uses cookies.
We use cookies to analyze website traffic and optimize your website experience. By accepting our use of cookies, your data will be aggregated with all other user data.